Routing DRC
Key DRC Constraints During Routing
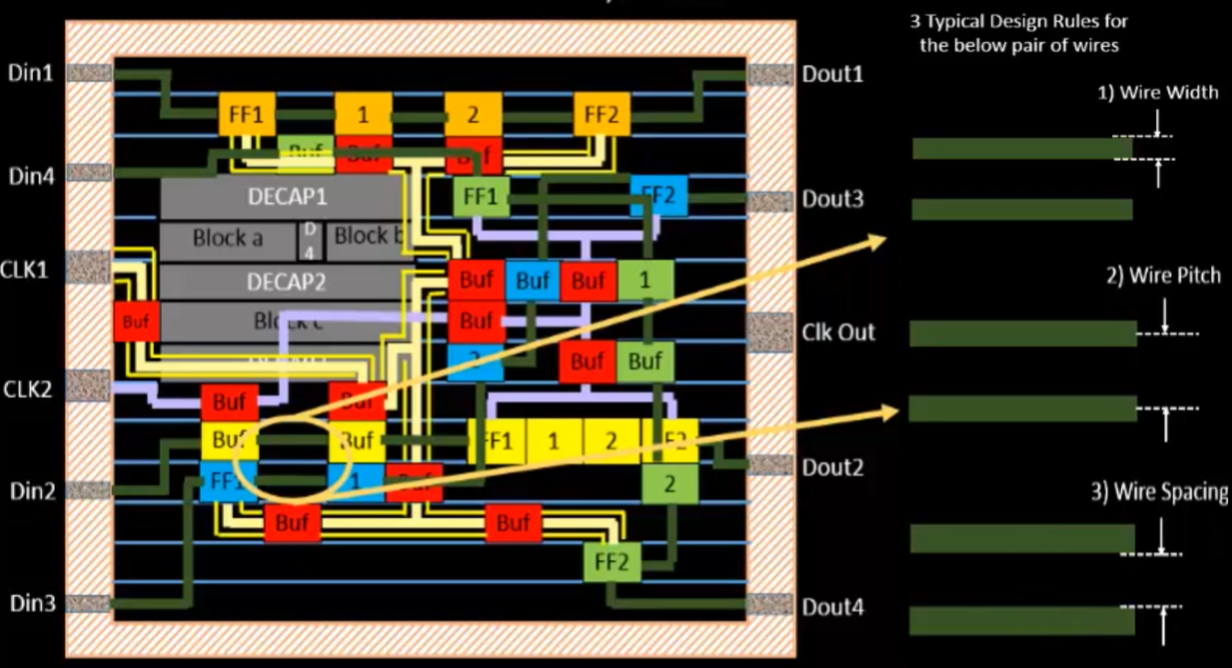
- Minimum Wire Width
- Ensures wires are thick enough to carry current without breaking or degrading during fabrication.
- Minimum Spacing Between Wires
- Prevents electrical shorts and crosstalk by maintaining enough distance between adjacent signal lines.
- Minimum Pitch
- Defines the sum of wire width + spacing, critical for density planning.
These rules are technology-dependent, defined by the foundry for each process node (e.g. 7nm, 5nm, etc.).
Signal Shorts and Layer Switching
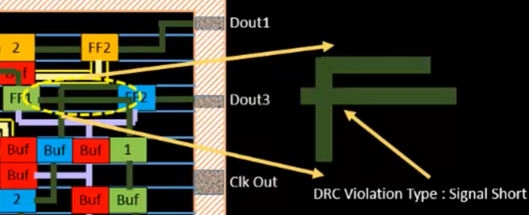
A common routing error is a signal short, where two nets accidentally touch. This leads to functional failure and must be avoided.
Fix
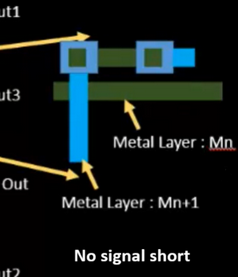
- Layer switching via vias is often used to bypass congestion or fix violations.
- However, this introduces new DRCs:
- Via Width and Spacing rules
- Metal Layer Width Scaling (higher metal layers usually require wider wires)
- Layer-to-layer alignment and density rules
DRC Cleaning
After initial routing, tools perform DRC cleaning to:
- Detect and fix violations (spacing, width, short, enclosure, etc.)
- Ensure that the layout meets all foundry manufacturing constraints
- Guarantee the design is printable and manufacturable in silicon
Only once a design is DRC-clean can it proceed to signoff and tape-out.